October 2021 |
Click on title to download full article
|
table of contents
articles
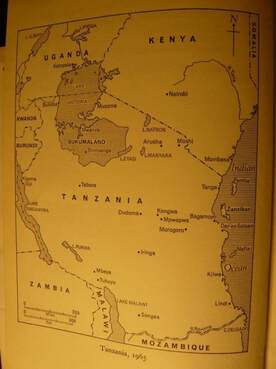
SMALL-SCALE GROWER'S STRUGGLE AGAINST MARGINALIZATION IN THE COTTON VALUE CHAIN. AN EXPERIENCE FROM THE WESTERN COTTON GROWING AREA, TANZANIA, 1920'S-1950'S
Source in the paper
Somo M. L. Seimu ([email protected])
This article analyses the marginalization of the native small-scale cotton growers during British colonial rule in the Western Cotton Growing Area (WCGA), Tanzania, and their struggle against it. Marginalization was practiced mainly by Indian cotton traders for three decades to maximize profit at the expense of natives who farmed the crop. The Indian traders who were licensed by the colonial authority to buy and export marginalized the growers through underpaying and cheating on them. From the 1930s local chiefs and their subjects (growers) began to protest against this situation, but were ignored by the colonial authority. At the end of the 1940s, growers formed groups which took initiatives that led to minimized marginalization with limited support from some colonial officials. Minimized marginalization did not imply control of the cotton value chain. With the support of native traders, local growers fought on until co-operatives were formed, which allowed them to gain the upper hand over the Indian merchants in the cotton value chain. (Paper in English)
This article analyses the marginalization of the native small-scale cotton growers during British colonial rule in the Western Cotton Growing Area (WCGA), Tanzania, and their struggle against it. Marginalization was practiced mainly by Indian cotton traders for three decades to maximize profit at the expense of natives who farmed the crop. The Indian traders who were licensed by the colonial authority to buy and export marginalized the growers through underpaying and cheating on them. From the 1930s local chiefs and their subjects (growers) began to protest against this situation, but were ignored by the colonial authority. At the end of the 1940s, growers formed groups which took initiatives that led to minimized marginalization with limited support from some colonial officials. Minimized marginalization did not imply control of the cotton value chain. With the support of native traders, local growers fought on until co-operatives were formed, which allowed them to gain the upper hand over the Indian merchants in the cotton value chain. (Paper in English)
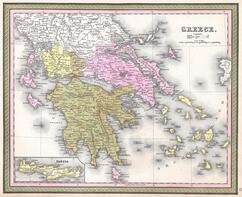
THE IMPORTANCE OF BEING GEORGE. CONSTITUTIONALISM AND KINGSHIP IN GREECE OF THE 1860'S AND EARLY 70'S
Source: Wikipedia
Lykourgos Sofoulis
The focus on this paper is the political history of Greece in the immediate aftermath of the ousting of the kingdom's first monarch, King Otto von Wittelsbach, and on to the first years of rule of his successor, King George I. After narrating the events that led to the installation of the new king, it specifically examines his cohabitation, inspired as he was by supposedly democratic ideals, with the fresh constitution of 1864; the challenges that the political and cultural landscape in the country presented for him, and the way he chose to respond in the first decade of his rule. (Paper in English)
The focus on this paper is the political history of Greece in the immediate aftermath of the ousting of the kingdom's first monarch, King Otto von Wittelsbach, and on to the first years of rule of his successor, King George I. After narrating the events that led to the installation of the new king, it specifically examines his cohabitation, inspired as he was by supposedly democratic ideals, with the fresh constitution of 1864; the challenges that the political and cultural landscape in the country presented for him, and the way he chose to respond in the first decade of his rule. (Paper in English)
"THEY SHALL NOT GROW OLD" AND "MIMESIS: AFRICAN SOLDIER". TECHNOLOGY, IDEOLOGY, AND REMEMBRANCE

Richard A. Voeltz
This paper will examine and compare two recent visual explorations of the experience of soldiers in World War I. Director Peter Jackson’s documentary They Shall Not Grow Old has been called an immersive, haunting and often transcendent experience that’s unlike anything you’ve ever seen before. By using modern digital film technology, he has restored the visuals and added sounds and speech via Automatic Dialogue Replacement, colorized, changed the speed, and brought 3D depth to the old footage from the Imperial War Museum. Jackson has either, using the terminology of William Guynn (Unspeakable Histories: Film and the Experience of Catastrophe), employed this technology to trigger “moments of heightened awareness in which the reality of the past may be recovered in its material being”. Or, do these computer generated technological affects, “….stand in for the ‘truth’ and obscure just how constructed the ‘history’ Jackson is telling actually is?” John Akomfrah’s video/sound three screen performance/display installation Mimesis: African Soldier uses silent actors, archive film and photographs, ethnographic sound recordings, new filmed footage with and without actors, and a sound track by Trevor Mathison, to document the experience of those, among many, left out of Jackson’s film: colonial subjects as soldiers. Akomfrah “does not put colour back in the cheeks of the dead”, but rather warns the viewer that remembrance can come in many forms, some of them unrealiable. All of this leads to a conclusion, as Avishai Margalit put it in Ethics of Memory, that “memory…is knowledge from the past. It is not necessarily knowledge about the past.” (Paper in English)
This paper will examine and compare two recent visual explorations of the experience of soldiers in World War I. Director Peter Jackson’s documentary They Shall Not Grow Old has been called an immersive, haunting and often transcendent experience that’s unlike anything you’ve ever seen before. By using modern digital film technology, he has restored the visuals and added sounds and speech via Automatic Dialogue Replacement, colorized, changed the speed, and brought 3D depth to the old footage from the Imperial War Museum. Jackson has either, using the terminology of William Guynn (Unspeakable Histories: Film and the Experience of Catastrophe), employed this technology to trigger “moments of heightened awareness in which the reality of the past may be recovered in its material being”. Or, do these computer generated technological affects, “….stand in for the ‘truth’ and obscure just how constructed the ‘history’ Jackson is telling actually is?” John Akomfrah’s video/sound three screen performance/display installation Mimesis: African Soldier uses silent actors, archive film and photographs, ethnographic sound recordings, new filmed footage with and without actors, and a sound track by Trevor Mathison, to document the experience of those, among many, left out of Jackson’s film: colonial subjects as soldiers. Akomfrah “does not put colour back in the cheeks of the dead”, but rather warns the viewer that remembrance can come in many forms, some of them unrealiable. All of this leads to a conclusion, as Avishai Margalit put it in Ethics of Memory, that “memory…is knowledge from the past. It is not necessarily knowledge about the past.” (Paper in English)
Reviews
Fernández Peña, Marta, Ciudadanos, electores y representantes. Discursos de inclusión y exclusión políticas en Perú y Ecuador (1860-1870) (Universitat de València, 2020), ressenyat per Miguel Adolfo Galindo Pérez.